Ten years of research on extracellular vesicles derived from mesenchymal cells for the treatment of lung diseases
Rescala, Gonzalo1; Ramos-de la Cruz, Ramiro1; Robles, Mónica1
Rescala, Gonzalo1; Ramos-de la Cruz, Ramiro1; Robles, Mónica1
ABSTRACT
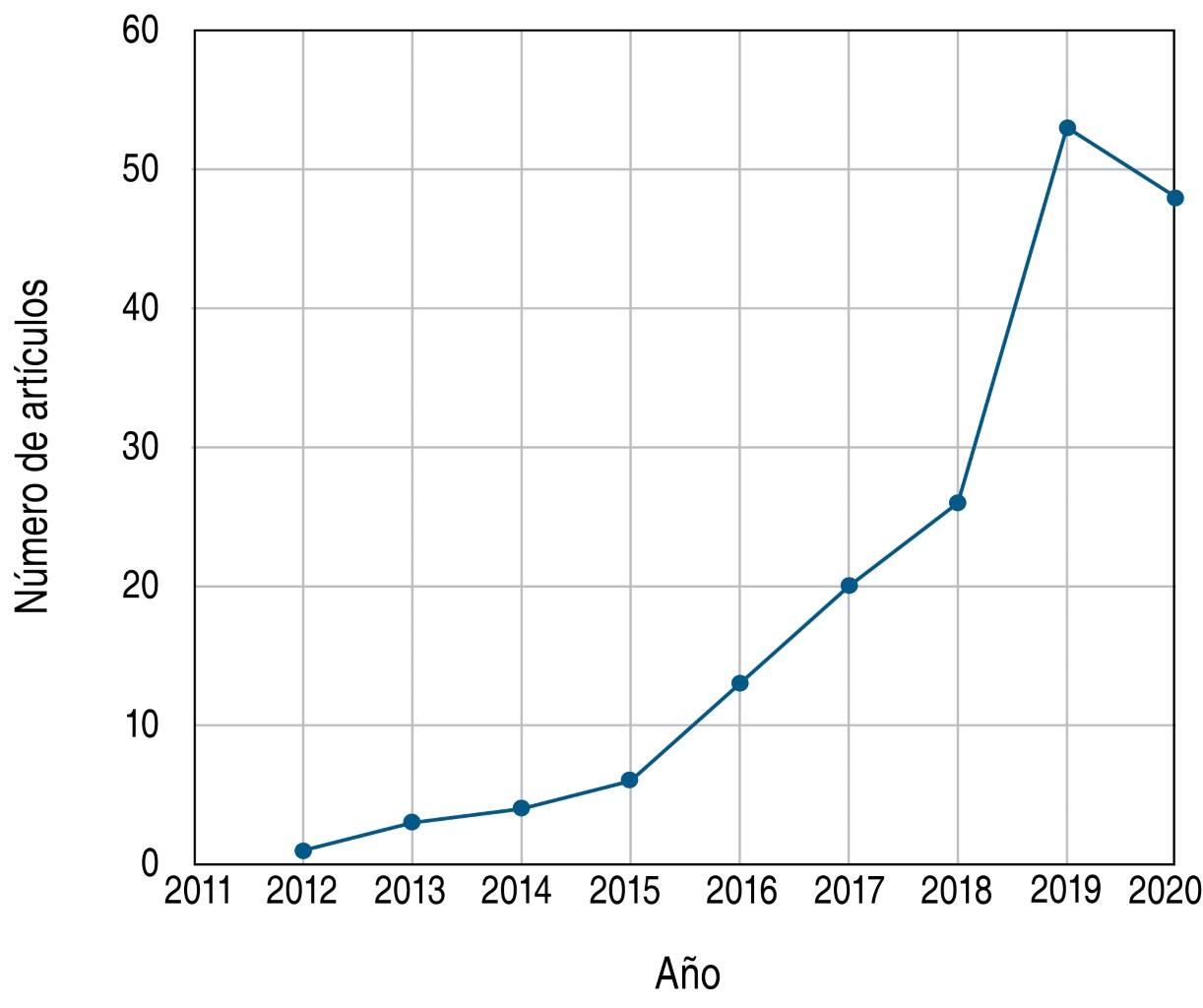
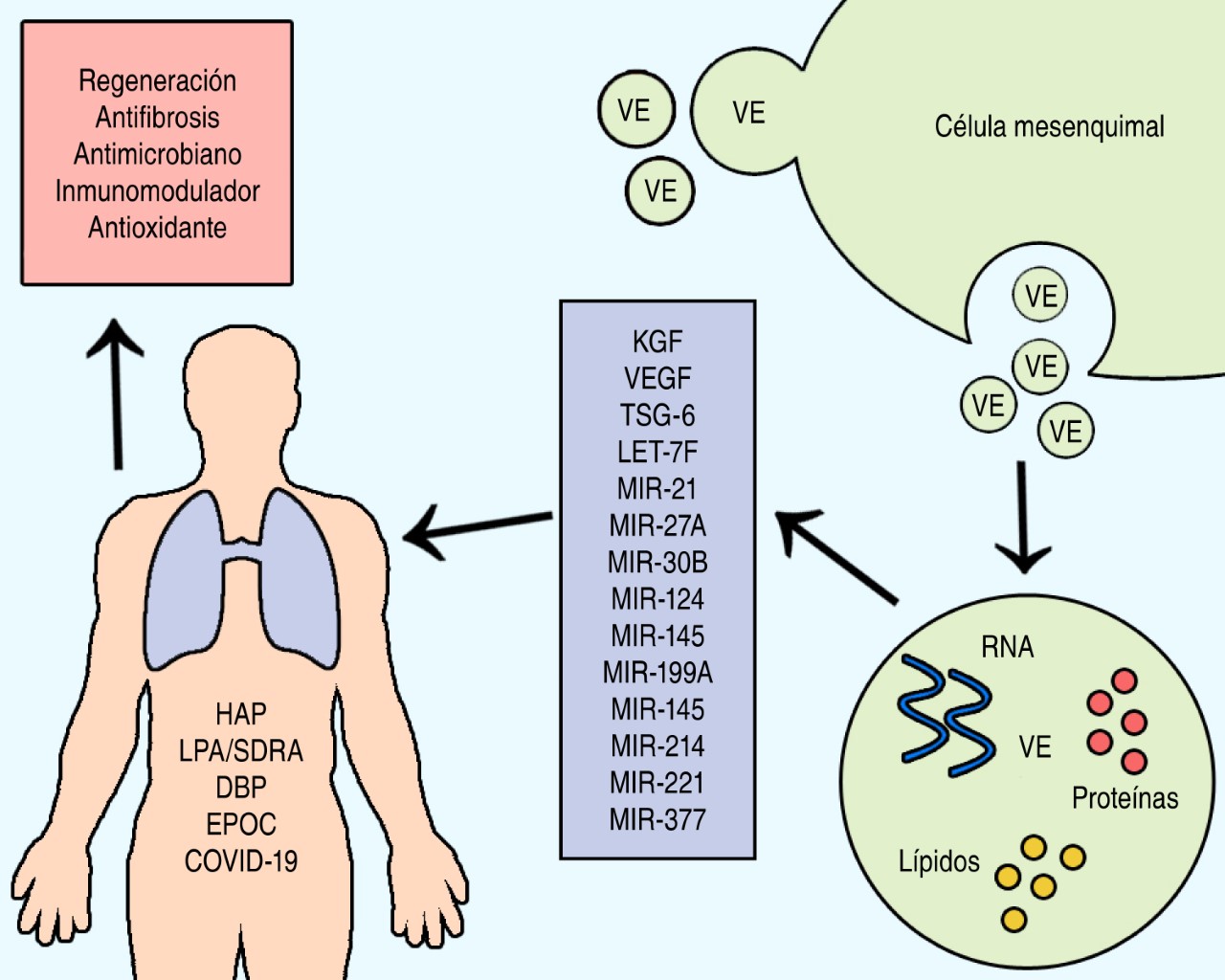
Pulmonary diseases possess high rates of morbidity and mortality throughout the world and without effective treatment for these diseases, new options emerge. In the last decade, attention has focused on extracellular vesicles derived from stromal mesenchymal cells (VECM) due to their immunomodulatory, regenerative, antimicrobial, antiviral and antifibrotic properties that surpass the properties of mesenchymal stromal cells themselves. Consequently, we present this review with the purpose of gathering the knowledge generated in the 10 years of research on the therapeutic application of VECM in pulmonary pathologies, including the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) that has plagued the world in the past months. The information presented in this article demonstrates that although further research is required to fully elucidate their mechanisms of action and efficacy, VECM represent a promising therapy option for the treatment of a wide variety of lung diseases.KEYWORDS
Extracellular vesicles, exosomes, mesenchymal stromal cells, lung diseases, COVID-19.REFERENCES
Kassebaum NJ, Arora M, Barber RM, Bhutta ZA, Brown J, Carter A, et al.; GBD 2015 DALYs and HALE Collaborators. Global, regional, and national disability-adjusted life-years (DALYs) for 315 diseases and injuries and healthy life expectancy (HALE), 1990-2015: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2015. Lancet. 2016; 388(10053): 1603-1658. Available in: https://doi.org/10.1016/s0140-6736(16)31460-x
Hoeper MM, Kramer T, Pan Z, Eichstaedt CA, Spiesshoefer J, Benjamin N, et al. Mortality in pulmonary arterial hypertension: prediction by the 2015 European pulmonary hypertension guidelines risk stratification model. Eur Respir J. 2017; 50(2): 1700740. Available in: https://doi.org/10.1183/13993003.00740-2017
Wang H, Naghavi M, Allen C, Barber RM, Bhutta ZA, Carter A, et al.; GBD 2015 Mortality and Cause of Death Collaborators. Global, regional, and national life expectancy, all-cause mortality, and cause-specific mortality for 249 causes of death, 1980–2015: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2015. Lancet. 2016; 388(10053): 1459-1544. Available in: https://doi.org/10.1016/s0140-6736(16)31012-1
Kotani T, Masutani R, Suzuka T, Oda K, Makino S, Ii M. Anti-inflammatory and anti-fibrotic effects of intravenous adipose-derived stem cell transplantation in a mouse model of bleomycin-induced interstitial pneumonia. Sci Rep. 2017; 7(1): 14608. Available in: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-15022-3
Lotvall J, Hill AF, Hochberg F, Buzás EI, Di Vizio D, Gardiner C, et al. Minimal experimental requirements for definition of extracellular vesicles and their functions: a position statement from the International Society for Extracellular Vesicles. J Extracell Vesicles. 2014; 3: 26913. https://doi.org/10.3402/jev.v3.26913
Théry C, Witwer KW, Aikawa E, Alcaraz MJ, Anderson JD, Andriantsitohaina R, et al. Minimal information for studies of extracellular vesicles 2018 (MISEV2018): a position statement of the International Society for Extracellular Vesicles and update of the MISEV2014 guidelines. J Extracell Vesicles. 2018; 7(1): 1535750. Available in: https://doi.org/10.1080/20013078.2018.1535750
Morrison TJ, Jackson MV, Cunningham EK, Kissenpfennig A, McAuley DF, O'Kane CM, et al. Mesenchymal stromal cells modulate macrophages in clinically relevant lung injury models by extracellular vesicle mitochondrial transfer. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2017; 196(10): 1275-1286. Available in: https://doi.org/10.1164/rccm.201701-0170oc
Baber SR, Deng W, Master RG, Bunnell BC, Taylor BK, Murthy SN, et al. Intratracheal mesenchymal stem cell administration attenuates monocrotaline-induced pulmonary hypertension and endothelial dysfunction. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2007; 292(2): H1120-H1128. Available in: https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpheart.00173.2006
Humbert M, Sitbon O, Chaouat A, Bertocchi M, Habib G, Gressin V, et al. Survival in patients with idiopathic, familial, and anorexigen-associated pulmonary arterial hypertension in the modern management era. Circulation. 2010; 122(2): 156-163. Available in: https://doi.org/10.1161/circulationaha.109.911818
Aliotta JM, Pereira M, Wen S, Dooner MS, Del Tatto M, Papa E, et al. Bone marrow endothelial progenitor cells are the cellular mediators of pulmonary hypertension in the murine monocrotaline injury model. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2017; 6(7): 1595-1606. Available in: https://doi.org/10.1002/sctm.16-0386
Willis GR, Fernandez-Gonzalez A, Anastas J, Vitali SH, Liu X, Ericsson M, et al. Mesenchymal stromal cell exosomes ameliorate experimental bronchopulmonary dysplasia and restore lung function through macrophage immunomodulation. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2018; 197(1): 104-116. Available in: https://doi.org/10.1164/rccm.201705-0925oc
Ahn SY, Park WS, Kim YE, Sung DK, Sung SI, Ahn JY, et al. Vascular endothelial growth factor mediates the therapeutic efficacy of mesenchymal stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles against neonatal hyperoxic lung injury. Exp Mol Med. 2018; 50(4): 1-12. Available in: https://doi.org/10.1038/s12276-018-0055-8
Porzionato A, Zaramella P, Dedja A, Guidolin D, Van Wemmel K, Macchi V, et al. Intratracheal administration of clinical-grade mesenchymal stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles reduces lung injury in a rat model of bronchopulmonary dysplasia. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2019; 316(1): L6-L19. Available in: https://doi.org/10.1152/ajplung.00109.2018
Willis GR, Fernandez-Gonzalez A, Reis M, Yeung V, Liu X, Ericsson M, et al. Mesenchymal stromal cell-derived small extracellular vesicles restore lung architecture and improve exercise capacity in a model of neonatal hyperoxia-induced lung injury. J Extracell Vesicles. 2020; 9(1). 1790874. Available in: https://doi.org/10.1080/20013078.2020.1790874
Chaubey S, Thueson S, Ponnalagu D, Alam MA, Gheorghe CP, Aghai Z, et al. Early gestational mesenchymal stem cell secretome attenuates experimental bronchopulmonary dysplasia in part via exosome-associated factor TSG-6. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2018; 9(1):173. Available in: https://doi.org/10.1186/s13287-018-0903-4
Le Thi Bich P, Nguyen Thi H, Dang Ngo Chau H, Phan Van T, Do Q, Dong Khac H, et al. Allogeneic umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cell transplantation for treating chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: a pilot clinical study. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2020; 11(1): 60. Available in: https://doi.org/10.1186/s13287-020-1583-4
Taghavi-Farahabadi M, Mahmoudi M, Soudi S, Hashemi SM. Hypothesis for the management and treatment of the COVID-19-induced acute respiratory distress syndrome and lung injury using mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes. Med Hypotheses. 2020;144: 109865. Available in: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mehy.2020.109865
Chen J, Hu C, Chen L, Tang L, Zhu Y, Xu X, et al. Clinical study of mesenchymal stem cell treatment for acute respiratory distress syndrome induced by epidemic Influenza A (H7N9) infection: a hint for COVID-19 treatment. Engineering (Beijing). 2020; 6(10): 1153-1161. Available in: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eng.2020.02.006
Matthay MA, Calfee CS, Zhuo H, Thompson BT, Wilson JG, Levitt JE, et al. Treatment with allogeneic mesenchymal stromal cells for moderate to severe acute respiratory distress syndrome (START study): a randomised phase 2a safety trial. Lancet Respir Med. 2019; 7(2): 154-162. Available in: https://doi.org/10.1016/s2213-2600(18)30418-1
Liao G, Zheng K, Lalu MM, Fergusson DA, Allan DS. A scoping review of registered clinical trials of cellular therapy for COVID-19 and a framework for accelerated synthesis of trial evidence-FAST evidence. Transfus Med Rev. 2020; 34(3): 165-171. Available in: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tmrv.2020.06.001