The Lean model on the pulmonary lobectomy process: results and pitfalls of a continuous journey
Almanzo, Santiago; Defranchi, Sebastián; Bertolotti, Alejandro; Parrilla, Gustavo; Martínez, Viviana; Favaloro, Roberto
Almanzo, Santiago; Defranchi, Sebastián; Bertolotti, Alejandro; Parrilla, Gustavo; Martínez, Viviana; Favaloro, Roberto
ABSTRACT
Objetivo: Describir los resultados de la implementación de la metodología «Lean» para lobectomía. Material y métodos: En 2012 comenzó una iniciativa hospitalaria para mejorar la eficiencia, aplicando el modelo «Lean» en el servicio de cirugía torácica. Se mapearon procesos, eliminando pasos sin valor e identificando oportunidades de mejora. Se evaluó y comparó el impacto en pacientes sometidos a lobectomía en tres períodos: referencia, 2008 a 2012 (período 1); implementación, 2013 a 2014 (período 2); e implementación completa, 2015 a 2018 (período 3). Resultados: 178 lobectomías: 70, 29 y 79 durante cada período. La edad media fue de 60.29 ± 12.25 años; 99-178 (55.6%) eran hombres. La estancia hospitalaria disminuyó durante el período 3 (6 versus 8 versus 4 días; p ‹ 0.001). Las complicaciones mayores aumentaron durante el período 2 (8.6 versus 24.1 versus 7.6%; p = 0.036) y se estabilizaron posteriormente. No hubo diferencias en la mortalidad a los 30 días ni en las tasas de reingreso. El margen de contribución económica directa mejoró (-0.35 a 9.51%; p = 0.002). Conclusiones: El modelo «Lean» puede disminuir la estadía hospitalaria y mejorar el margen de contribución directa. Se debe minimizar el impacto negativo que podrían tener los cambios en los estándares prevalecientes.KEYWORDS
Lobectomía, mejora de procesos, metodología Lean.Introduction
Lean is a methodology that aims to increase productivity by eliminating those steps which do not add value to a certain process. The concept of Lean was conceived by Toyota engineer Taiichi Ohno in the car manufacturing industry in the mid-seventies and has evolved into a management philosophy. Toussaint et al. defined Lean in health care as "an organization's cultural commitment to applying the scientific method to designing, performing, and continuously improving the work delivered by teams of people, leading to measurably better value for patients and other stakeholders".1 In health care there are publications describing the Lean implementation in the operating room processes,2 in esophagectomy patients,3 in medical centers4,5 and more recently, in lung surgery.6,7 In the actual environment of health care value,8 improving outcomes while containing or decreasing costs have become a main concern. The Lean model appears as a methodology to achieve this. While the model could be used in any hospital area, in this particular case, we report its use and results as an improvement tool for the lobectomy. As such, the objective of this study is to report our experience with the implementation of the Lean model in the pulmonary lobectomy process at a general thoracic surgery service in tertiary care academic medical center.
Material and methods
Our hospital is a 180 beds tertiary care academic facility located in downtown Buenos Aires, Argentina. It is one of highest volume transplant centers in Argentina.
In mid-2012, the hospital deployed a top-down strategic plan which aimed to improve hospital finances while increasing patient related outcomes. Three periods were defined: a baseline period from June 2008 to December 2012 (period 1); the lean implementation period, from January 2013 to December 2014 (period 2); and the full Implementation period, from January 2015 to June 2018 (period 3). A two-year period was considered enough time for all stakeholders to buy-in and be familiar with the lean model. Period 1 recorded metrics were followed up and compared to the same metrics during period 2 and 3; financial data was analyzed when available.
Lobectomy was selected as it is the most common major general thoracic surgery procedure. Also, The Society of Thoracic Surgeons (STS) selected this procedure for its first thoracic quality measure.9 Patients who underwent pulmonary lobectomy between June 2008 and June 2018 were selected from a prospectively maintained general thoracic surgery database. Prospectively collected data included, but were not limited to patient demographics, clinical presentation, radiologic findings, pathology report, type of surgical approach (open versus vide o-assisted thoracoscopic surgery -VATS-), complications, length of stay (LOS), length of chest tube drainage, mortality, surgical time and 30-day readmissions.
Lean is a toolkit consisting of various methodologies, like the value streaming map, a step by step representation of a process.10 A multidisciplinary team was assembled to develop it: thoracic surgeons, nurses, scrub nurses, pharmacists, administrative and information technology (IT) staff. Within the value streaming map, subsets of activities were identified: pre-operative evaluation; admission and business office; surgical scheduling; surgical procedure; hospital care; discharge and follow-up. Different teams focused on each one of the activities. For pulmonary lobectomy and for this report, focus was on (1) pre-operative evaluation, (2) surgical scheduling, (3) surgical procedure and (4) hospital care. Processes were mapped and each process' step was evaluated on whether it added value or not to the process. Value was defined as something that was strictly necessary to be done and could not be eliminated.
Root-Cause Analysis (RCA) and the Plan-Do-Check-Act (PDCA) improving cycle or Deming Cycle are two other tools that are core to the lean methodology.11 PDCA cycle is a methodic procedure which has a special emphasis on the Plan phase. In the Plan phase of the cycle, key performance indicators (KPI) are measured and a root cause is sought for improvement using the RCA. The improvement measure is implemented in the Do phase. KPIs are measured again during the Check phase of the PDCA cycle to determine whether the process has been improved or nor. If an improvement has indeed occurred, the improvement measure is established as the new standard in the Act phase, closing the PDCA cycle.
KPIs were selected based on the baseline recorded data that were available to review. Among them were: overall complications, major complications, mortality, duration of surgery, length of chest tube drainage, hospital LOS, 30-days readmission rate and percentage of economic margin. Complications were defined as those more than grade II in the Clavien-Dindo Classification.12 Major complications were defined as per the STS metrics for star rating, which include: pneumonia, acute distress respiratory syndrome (ARDS), bronchopleural fistula (BPF), pulmonary embolism (PE), ventilator support longer than 48 hours after surgery, reintubation, tracheostomy, myocardial infarction and unexpected reoperation.9 Mortality was defined as the one that occurred prior to discharge or within 30-days of surgery. The economic result was defined as the difference between the revenue from the procedure and the direct costs incurred to do it. Because of high inflation in Argentina, which makes temporal absolute measurements inaccurate, a margin percentage was calculated.
As a process measurement tool, control charts were used. Control charts are analytical tools used in the Six Sigma methodology.
Findings and Interventions
Statistical analysis
Descriptive statistics were shown by the use of mean, median, standard deviation, 25-75 interquartile range and frequency, as appropriate. Statistical testing was performed on SPSS software (IBM SPSS Statistics Version 25, IBM Corporation, Armonk, NT, United States).
Results
During the study period 178 lobectomies were performed: 70, 29 and 79 patients were performed in period 1, 2 and 3, respectively. Mean age was 60.29 ± 12.25 years; 99/178 (55.6%) were males. Overall major complications occurred in 19/178 (10.7%) and 30-day mortality rate was 5/178 (2.8%). Patients' demographics in each period are presented in Table 1.
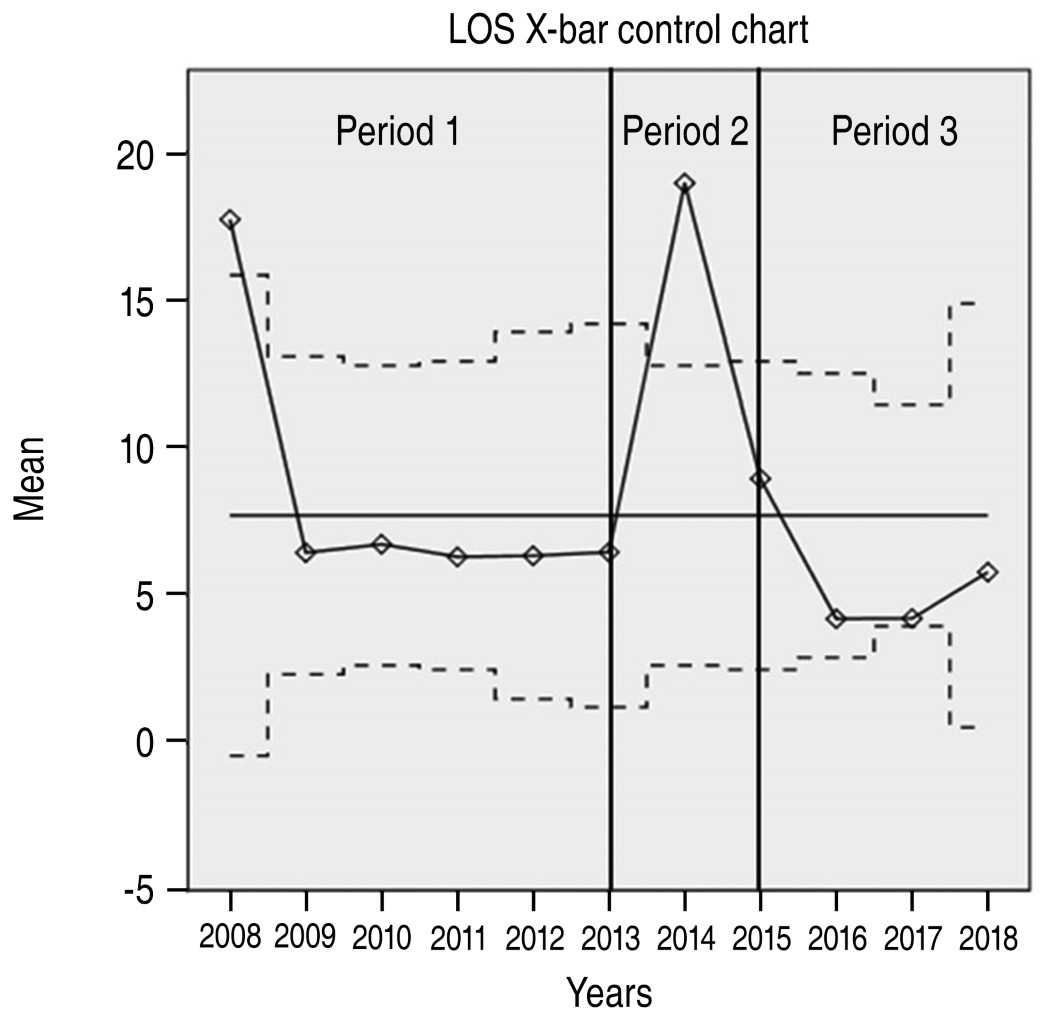
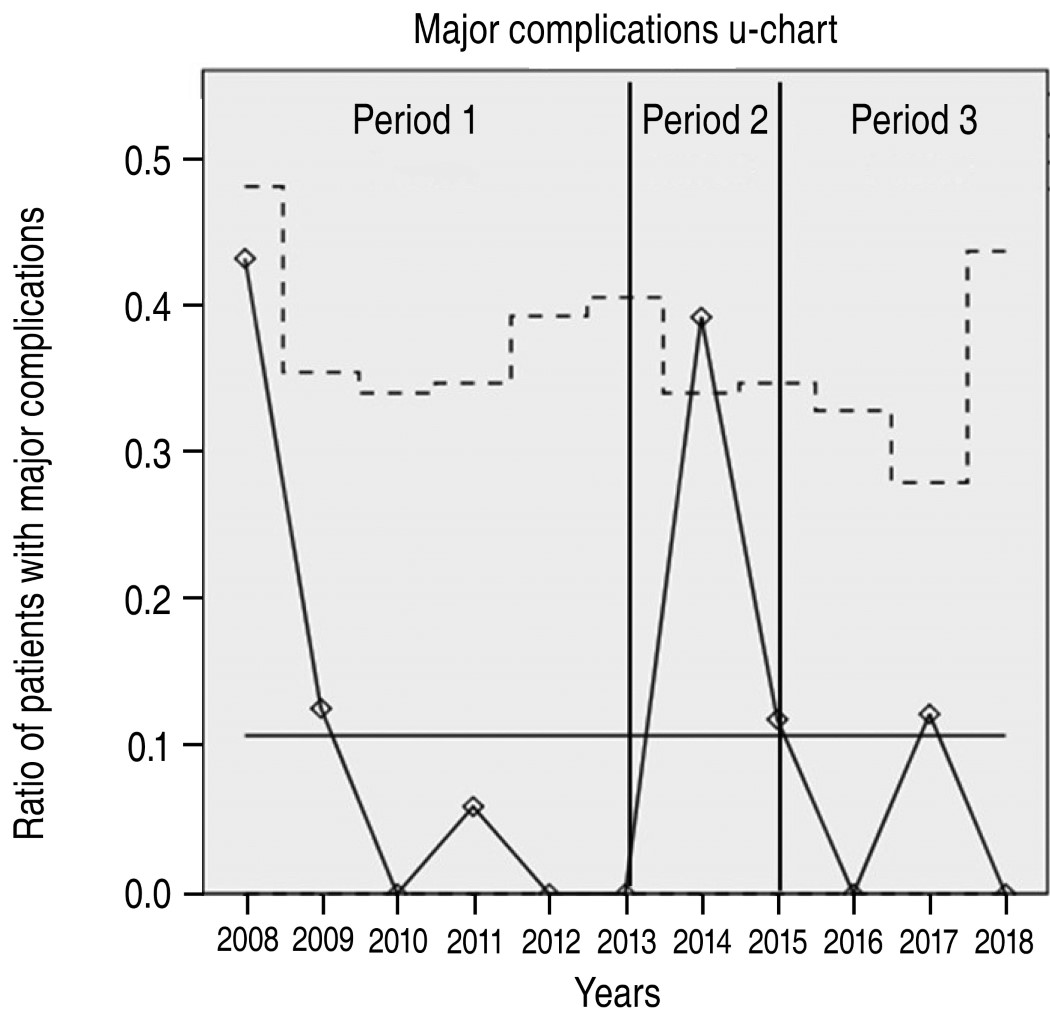
Table 2 shows operative and postoperative results. Of note, hospital length of stay (LOS) decreased significantly during period 3 (6 versus 8 versus 4 days; p < 0.001). Major complications peaked significantly in period 2 (8.6 versus 24.1 versus 7.6%; p = 0.036) and stabilized thereafter. There were no differences in 30-day mortality (1 versus 2 versus 2; p = 0.319) and readmission rates (7 versus 1 versus 9; p = 0.455) between periods. Direct contribution margin improved significantly from period 2 to period 3 (-0.35 to 9.51%; p = 0.002). The number of patients that were discharged by post-operative day #3 was significantly higher during period 3 (11.4 versus 6.9 versus 44.3%; p < 0.001).
Figures 1 and 2 shows control charts for selected processes. The hospital LOS X-bar (Figure 1) and the complications u-chart (Figure 2) show special cause of variations during period 2. These variations disappeared in period 3.
Discussion
The motivation behind this implementation was a hospital endeavor to improve finances while improving patients' outcomes started back in 2012. The Lean model is a management philosophy that it is recommended to be funneled through the whole organization with a top-down approach.4,5,10 Unfortunately, this was not the case for our study as the lean model was only used as a model for quality improvement in the OR and our general thoracic surgery service.
Cima and colleagues described the use of Lean to improve OR efficiency at the Mayo Clinic in Rochester.2 In their study, the creation of a Surgical Process Improvement Team to identify and implement improvement measures, improved on-time starts and OR operating margin. Cerfolio and colleagues reported the results of a Lean implementation in pre-incision time for pulmonary lobectomy,6 while Iannettoni described the use of Lean for esophagectomy patients.3 The value of our study lies in that it has been done in a different environment than the previous reports and our findings are still similar. Argentina has an allied health care staff force heavily unionized which might offer some hurdles at the time of introducing labor changes. Also, inflation is a chronic problem in the country which makes strategic planning a real challenge. With these caveats in mind, achieving high efficiency is a high priority to keep a financially viable organization. This is where the lean methodology fits in.
Our main findings were that after the Lean implementation the hospital LOS decreased from a median of 6 to 4 days (p > 0.001), while the direct economic margin improved from a negative -0.35% to a positive 9.51% (p = 0.002). Unfortunately, we did not have a detailed case by case financial data of patients that were operated during period 1. However, we knew from our administrative records, that the margin for lobectomy was considered negative during period 1.
By the end of the study period, no significant increase in morbidity or mortality was observed. Also, something as simple as setting an explicit objective date for discharge, eased to meet the target in 44.3% of patients during period 3.
Of note is how major complications and hospital LOS increased during period 2. We do not have a certain explanation for these findings, but we can hypothesize that proposed changes were not welcomed when first introduced. However, we cannot specify how these changes lead to an increase in major complications. Changing an established practice is a slow process that can only be attained when the main stakeholders feel that they are part of the process. This is why we gather multidisciplinary teams to map and analyze the processes, taking a period of two years to implement changes.
We observed no problems associated with the removal of any of the elements that were eliminated.
Once a process has been mapped, it is important to choose the right metrics to measure it. The metric definition and how the measurement will take place should be specifically defined and communicated among the stakeholders. When metrics are not correctly defined or doubt arises on how the data is collected, trust is lost and it is very difficult or even impossible to restore it. This is why we choose fairly simple performance metrics to follow our processes. Also, we had the constraint of choosing metrics which we have already been measuring in period 1.
Control charts provide a visual clue on how a process is performing and offers objective evidence on special causes of variation. Special variation is spotted on control charts as recordings outside the control limits. In the case of our study, a special variation was visualized on major complications during the Lean implementation phase. The suspected cause for special variation was the Lean implementation itself. Despite it raised our concerns, after reviewing each process' step that we had eliminated or had changed, we still believed we could improve our process by the use of lean and we kept pursuing the objective. Another possible cause of special variation was that by the same time, a strategic plan that was being deployed in the whole Institution. Economic results for each individual surgical group had started to be monitored and reported. Certainly, this created some strain in the hospital staff as it was a practice that has never being done before. We cannot draw definite conclusions about the relationship between these facts and our results, but our hypothesis is that some association could have existed.
Our study has limitations which we should recognize. Despite the study time frame extends over 10 years, the number of lobectomies during some periods was fairly low to draw definitive conclusions. However, it is important to note how some metrics deteriorated during the Lean implementation period.
Inspired by a recent report, we look for simplifying our surgical VATS tray.12 From an existing tray of 43 instruments and with the help of our scrub nurse, we reduced it to 16 instruments. More recently, we revised the provisions that are taken from the supply room to the OR and reduced the number by 57%. The monetary value reduction of the supplies that were not mobilized to the OR was 70%.
Value can be increased by improving patient related outcomes or by decreasing costs. Non-value added steps are a hidden source of costs. Every process can be mapped, reviewed and improved with the objective of providing better outcomes while reducing costs. The Lean methodology provides an effective frame-work to address both.
Conclusions
We showed how the Lean methodology can be used to improve the lobectomy process. It can result in decreased hospital LOS. However, introducing changes is not without risks as we evidenced during the Lean implementation period with a significant increase of major complications. Efforts should be directed to minimize the negative impact that challenging prevailing process could have.
AFILIACIONES
1General Thoracic Surgery Service, Hospital Universitario Fundación Favaloro, Ciudad de Buenos Aires, Argentina.REFERENCES
Cima RR, Brown MJ, Hebl JR, Moore R, Rogers JC, Kollengode A, et al; Surgical Process Improvement Team, Mayo Clinic, Rochester. Use of lean and six sigma methodology to improve operating room efficiency in a high-volume tertiary-care academic medical center. J Am Coll Surg. 2011;213(1):83-94. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jamcollsurg.2011.02.009
|
Table 1: Patient demographics per period. |
||||
|
Variable |
Baseline period (n = 70) June 2008-December 2012 |
Lean implementation period (n = 29) January 2013-December 2014 |
Full lean implementation period (n = 79) January 2015-June 2018 |
p |
|
Age, mean years (± SD) |
59.1 (13.5) |
60.9 (12.4) |
61.1 (11) |
0.59 |
|
Males, n (%) |
42 (60) |
16 (55.2) |
41 (51.9) |
0.61 |
|
VATS lobectomy, n (%) |
21 (30) |
7 (24.1) |
32 (40.5) |
0.19 |
|
Current smoker, n (%) |
15 (21.4) |
12 (41.4) |
21 (26.6) |
0.12 |
|
Body mass index, mean (±SD) |
26.7 (4.4) |
27.1 (4.7) |
26.84 (3.8) |
0.91 |
|
Comorbidities, n (%) |
|
|
|
|
|
Hypertension |
32 (45.7) |
11 (37.9) |
28 (35.4) |
0.43 |
|
Congestive heart failure |
2 (2.9) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
0.21 |
|
Coronary artery disease |
10 (14.3) |
1 (3.4) |
5 (6.3) |
0.12 |
|
Stroke |
0 (0) |
1 (3.4) |
2 (2.5) |
0.35 |
|
Diabetes |
8 (11.4) |
4 (13.8) |
7 (8.9) |
0.73 |
|
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease |
13 (18.6) |
5 (17.2) |
15 (19) |
0.97 |
|
Creatinine > 2 mg% |
1 (1.4) |
2 (6.9) |
1 (1.3) |
0.18 |
|
Previous cancer |
13 (18.6) |
5 (17.2) |
21 (26.6) |
0.40 |
|
Table 2: Postoperative results by period. |
||||
|
Variable |
Baseline period (n = 70) June 2008-December 2012 |
Lean implementation period (n = 29) January 2013-December 2014 |
Full lean implementation period (n = 79) January 2015-June 2018 |
p |
|
30-day readmission, n (%) |
7 (10) |
1 (3.4) |
9 (11.4) |
0.45 |
|
30-day mortality, n (%) |
1 (1.4) |
2 (6.9) |
2 (2.5) |
0.31 |
|
LOS, median days (percentile 25-75) |
6 (4-8) |
8 (5-12) |
4 (3-5) |
< 0.001 |
|
Margin, % |
N/A |
-0.035 (-0.63-0.31) |
9.51 (-1.46-35.68) |
0.002 |
|
Discharge by POD#3, n (%) |
8 (11.4) |
2 (6.9) |
35 (44.3) |
< 0.001 |
|
Surgical time, min (percentile 25-75) |
150 (120-180) |
180 (150-200) |
150 (115-165) |
< 0.001 |
|
Chest tube drainage time, days (percentile 25-75) |
4 (2-5) |
4 (3-6) |
3 (2-4) |
0.885 |
|
Complications, n (%) |
|
|
|
|
|
All complications |
19 (27.1) |
14 (48.3) |
20 (25.3) |
0.057 |
|
Major complications |
6 (8.6) |
7 (24.1) |
6 (7.6) |
0.036 |


